What is an attenuator?
An attenuator (ATT) is a resistive attenuator. It is like a kind of volume, and by turning the knob to the right and left, the level (intensity) of the sound changes to +/-. It can be continuously variable or a step type with a decibel scale.
Role in the Speaker
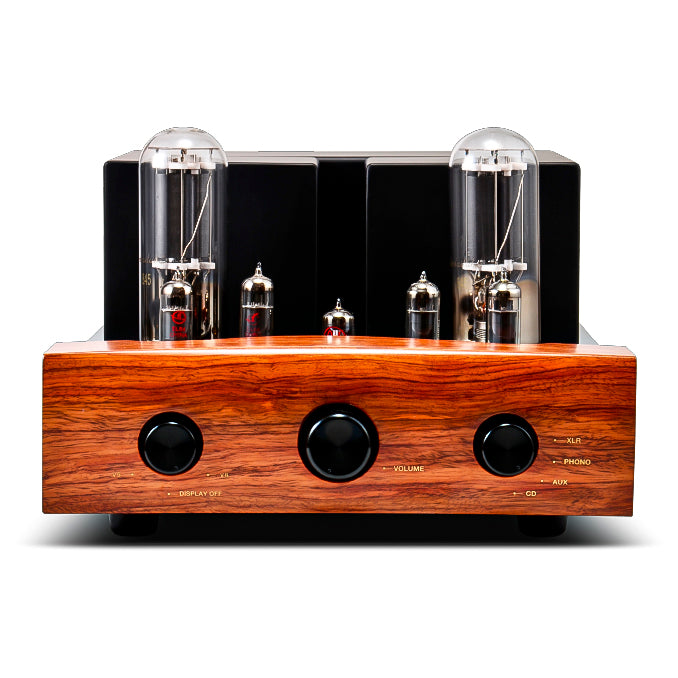
Click here for the speaker's product page
The way it is used in speakers is that the attenuator in the speaker fills in the level difference between the units that are configured, such as the woofer, squawker, and tweeter, and flattens the characteristics.

Speakers are usually designed for greater efficiency than woofers, so attenuators are included to adjust the level of squawkers and tweeters. You can adjust the level between units to your preferred level according to the conditions of the room where the audio is installed and the music genre you are listening to.
It seems that the types of speakers used in recent years are limited, and I don't see them very often. As is the case with the manufacturers we handle, it is unnecessary because the sound is tuned with high accuracy along with the network circuit inside the speaker.
Amplifier volume adjustment function
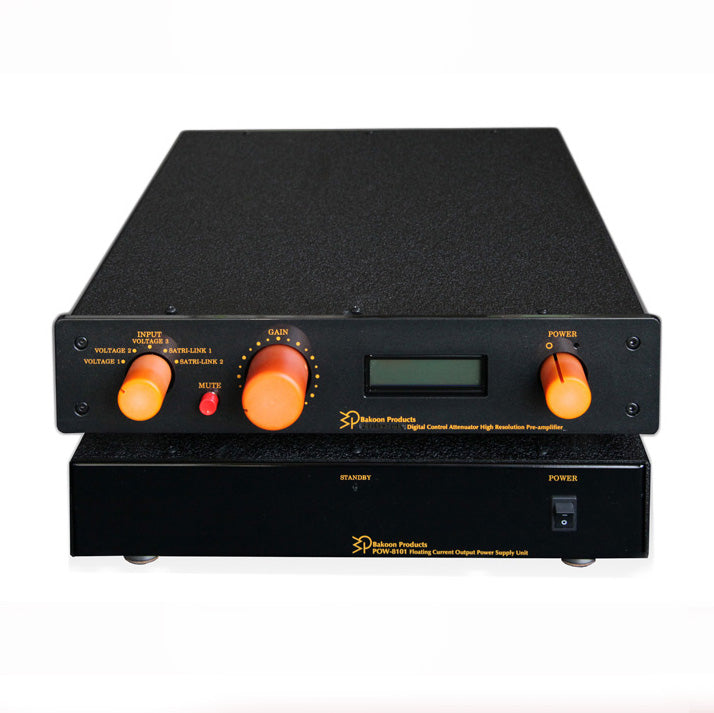
Click here for Bakun Products' preamplifier PRE-7610MK4 with a choice of attenuators.
Click here for Bakun Products' SCA-7511MK4 power amplifier with a choice of attenuators.
Another way to use an attenuator is to use it as a volume circuit in an amplifier, or to a "passive attenuator" that removes the amplification circuit from the amplifier, and is used in equipment that is particularly particular about sound quality and volume control functions.
The one used for amplifiers is generally a volume adjustment function, so you may think that the volume changes at most, but the attenuator is an excellent one that dramatically changes the sound just by changing it.
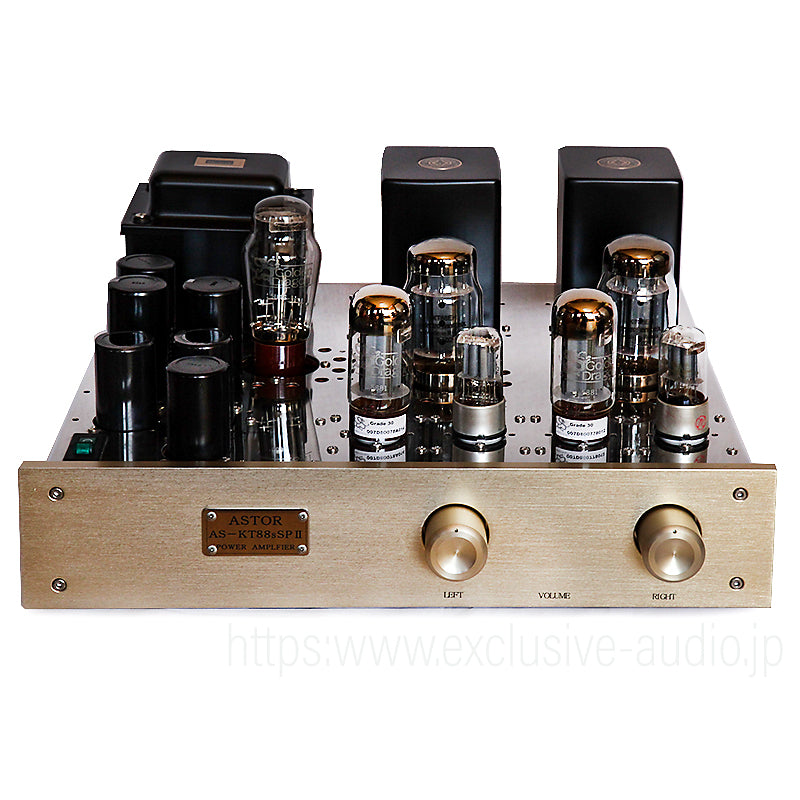
Click here for AS-XP88EZC AS-Preamplifier with attenuator.

By adopting an attenuator in the volume part of the amplifier, it is possible to reproduce high-definition and high-precision sound than the volume circuit normally used, providing music that is stretched and expressive. The accuracy of the reproduced sound also changes depending on the accuracy of the resistor. From the standard volume specifications such as the Bakun Products amplifier series, you can optionally choose a metal-film type resistor with low current noise, good accuracy, and excellent characteristics, and a non-inductive wire-wound resistor that greatly reduces the generation of parasitic inductance, which causes distortion (linking) of the signal waveform that occurs in the amplifier circuit with magnetic flux. As the accuracy of the resistance increases, so does the amount, but it is better to choose according to your preferred music genre.

Passive attenuator
Click here for Yamamoto Acoustic Craft's passive attenuator AT-03-1A
Click here for Yamamoto Acoustic Craft's passive attenuator AT-03-3A
A "passive attenuator" is a device with a volume adjustment mechanism that is very simply configured using only passive elements and passive elements, without using amplifying elements such as vacuum tubes and transistors or buffer circuits to transmit sound signals to the speakers and power amplifiers mounted in the amplifier. Since it does not require power and there is no amplification circuit, the low frequencies are often light when pressed side by side, but the passive attenuator, which is kept to the minimum necessary, has an appeal that is difficult to obtain with a preamp, such as the freshness and resolution of the sound, the rawness of the high frequencies, the amount of information, and the ease of exit.

It expresses the spineless high frequencies of wind instruments, the subtle changes in the touch of piano players, and the details of each note of violin and classical guitar strings. The light tone and moderate low frequencies are comfortable to listen to, and the passive attenuator, which is natural and delicate, has a lot of sound information and is fresh, especially for those who listen to classical music mainly in small groups or solo.